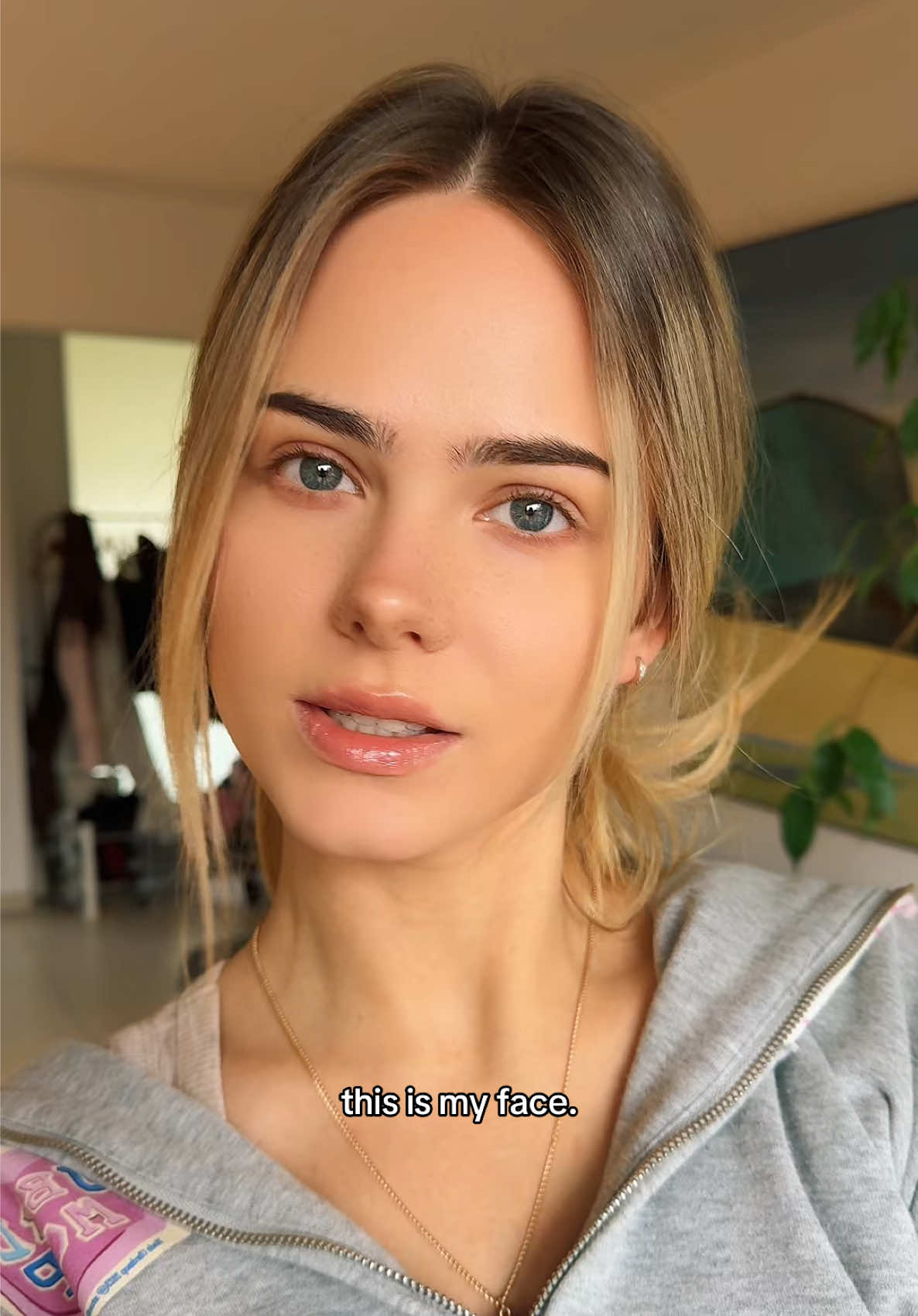
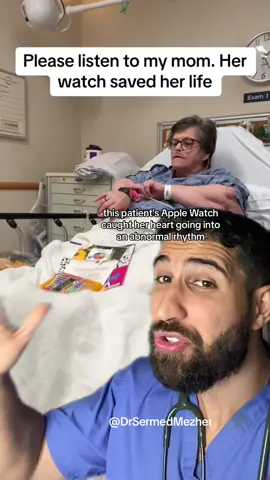
Anetta Orlova
Region: GB
Wednesday 26 June 2024 09:10:56 GMT
7962
157
4
4
Music
Download
Comments
Ekaterina :
это мой бывший😆
2024-06-26 11:14:42
1
ommnatasha :
вот у вас причёска всегда красивая
2024-08-21 17:24:49
0
Arkady Blyakher :
Вы имеете мужа? 😴
2024-07-09 23:37:24
0
Nino Rino :
я смотрела на кота😄
2024-07-04 13:30:18
0
To see more videos from user @anettaorlova, please go to the Tikwm
homepage.